
There are two variables that one of them is ‘a’ and the other one is ‘t’. In this one line of code, we inserted our differential equation inside the ‘dsolve()’ command. In the example above, you can see the most basic use of the ‘dsolve()’ command in Matlab®. How To Use ‘dsolve()’ Command In MatLab®? > s = dsolve('Da+t+a=sin(t)+t') Check these coding examples that are executed in the Matlab® command window, to understand the syntax and the use of the ‘dsolve()’ command. Here, we explain how to solve differential equations in Matlab® with the ‘dsolve()’ command with various coding examples below. You can solve differential equation systems also.

You can solve many differential equations in Matlab® by using the ‘dsolve()’ command. YOU CAN LEARN MatLab® IN MECHANICAL BASE Click And Start To Learn MatLab®! So, Matlab® provides very useful tools to solve these differential equations. In most cases, solving differential equations can be uneasy. Remember the order which with you enter coefficients in the code affect the result, and always remember to put 0 to indicate where the coefficient is not existent for lower exponents of the equation.In most engineering problems and situations, the governing mathematical facts are differential equations.
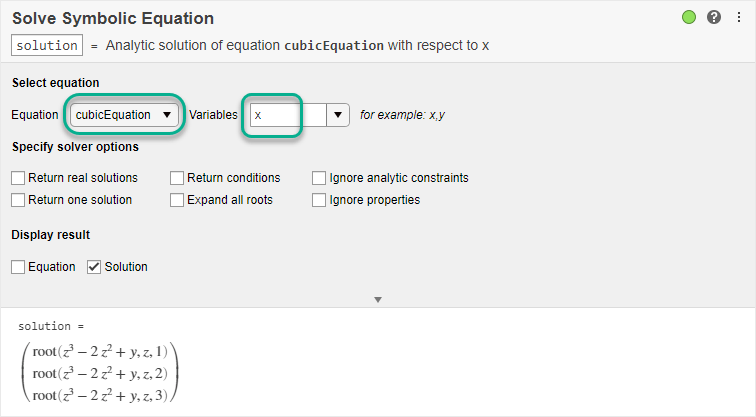

The higher-order the higher number of coefficients. The only difference here is that we have non-zero third-order coefficient to add to it roots()ĭo not forget to add 0 between 6 and -20 since the first-order coefficient is zero The line of code to solve it won’t be that different compared to the previous one. To solve this equation with Matlab you will enter the following code roots()Īnd Matlab will give you the roots of the polynomial equation Let’s go ahead and solve the following equation with Matlab So you will also find quadratic equations in the form


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
